What is Google Ads?
Google Ads is a comprehensive advertising service offered by Google, allowing businesses to display ads on Google and its advertising network. Advertisers bid to display brief advertisements, service offerings, product listings, or videos to web users. It can place ads both in the results of search engines like Google Search and on non-search websites, mobile apps, and videos. The platform offers a variety of ad formats, including search ads that appear on Google’s search engine results pages, display ads that show up on websites within Google’s network, and video ads that can be shown on YouTube and other partner platforms.
Why Choose Google Ads for Video Advertising?
Google Ads integrates seamlessly with YouTube, the second-largest search engine and the largest platform for video content. This synergy allows advertisers to benefit from YouTube’s massive user base, diverse content, and advanced analytics. With Google Ads, you can customize your video ad campaigns based on numerous factors like location, age, interest, and more, ensuring that your ads reach your intended audience.

Why Video Ads?
- Engagement: Video content is inherently more engaging than text or image-based content. Videos can tell a compelling story, display product functionality, or convey emotional appeal in a manner that is tough to achieve through other formats.
- Retention: Videos improve information retention. According to various studies, people remember 95% of a message when it is watched, whereas only 10% when read.
- Shareability: Videos are more likely to be shared across social media platforms. The ease with which viewers can share videos makes it a powerful tool for enhancing brand visibility and reach.
2. Types of Video Ads
In-Stream Ads
- Placement: In-stream ads are videos that play before, during, or after other videos on YouTube. This format allows your advertisement to be paired with related content, increasing the likelihood of engaging a receptive audience.
- Skippable and Non-Skippable: In-stream ads come in two types, skippable and non-skippable. Skippable ads can be skipped after 5 seconds, but advertisers are only charged if the viewer watches for at least 30 seconds or until the end of the video, whichever comes first.
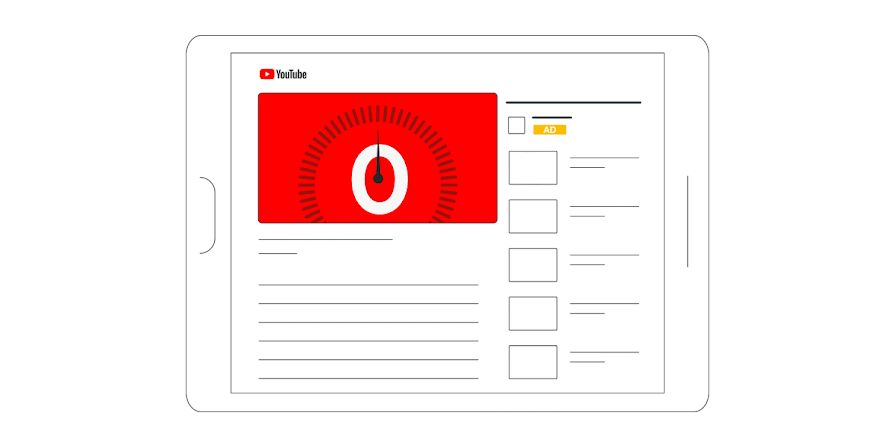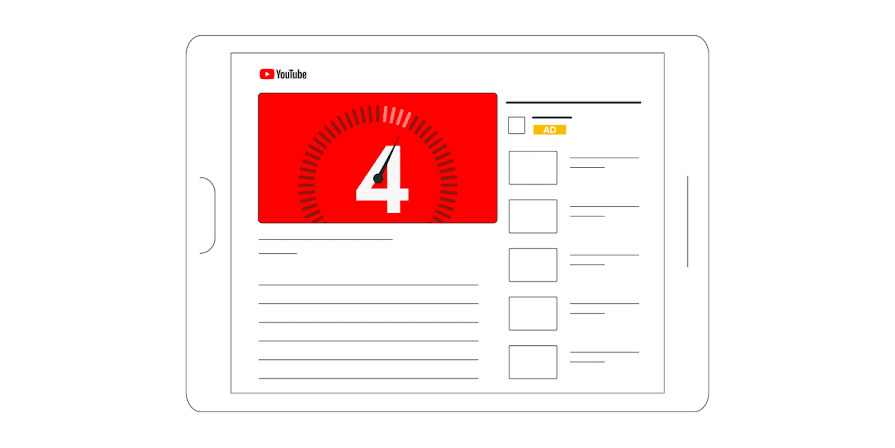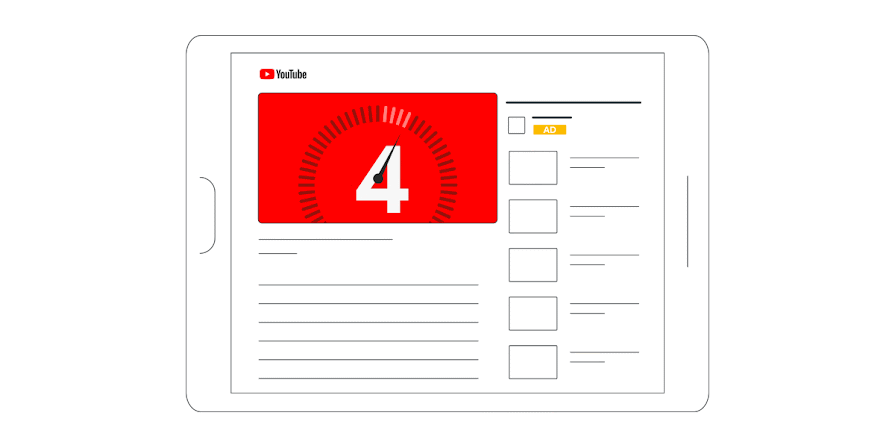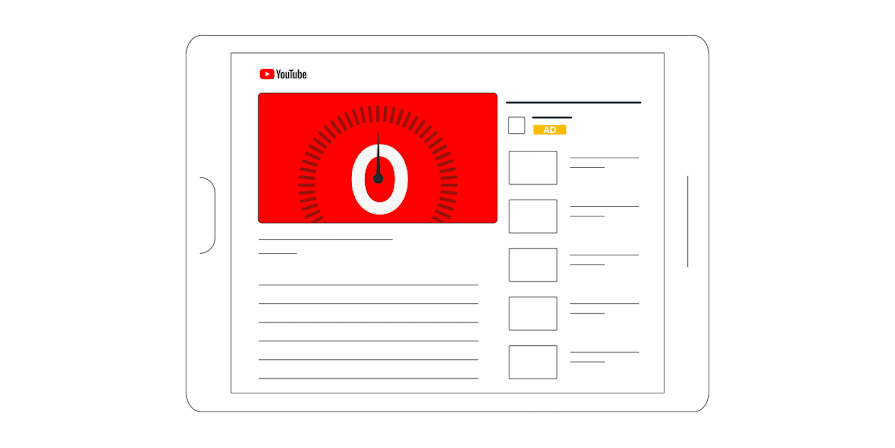
- Non-skippable ads are shorter and must be watched before the viewer can proceed to the video they selected. The choice between the two often depends on the campaign objectives; skippable ads are generally better for branding, while non-skippable ads are effective for call-to-action oriented campaigns.
- Best For: These are ideal for increasing brand awareness because they are typically paired with content that is already being viewed by your target audience.
Video Discovery Ads
- Placement: Video discovery ads are unique in that they appear in the YouTube search results or in the related videos section. Unlike in-stream ads, they aren’t played automatically, giving viewers the option to engage with the ad by clicking on it.
- Best For: This format is excellent for advertisers who have informational or tutorial content that users are actively searching for. It offers an element of user choice, as viewers choose to click and watch your ad, which can result in higher engagement rates.
Bumper Ads
- Placement: These short, non-skippable ads of up to 6 seconds are placed either at the beginning or end of YouTube videos. Their brevity ensures that your message is concise and to the point.
- Best For: Bumper ads are effective for brand recall and short, catchy messages. They are often used in conjunction with a broader video campaign to reinforce the message.
Outstream Ads
- Placement: Outstream ads are mobile-only video ads that serve on partner sites and apps outside of YouTube. These ads only start playing when 50% of the ad is viewable and are optimized for mobile screen dimensions. Advertisers are billed on a vCPM basis.
- Best For: If you are looking to expand your mobile reach without being confined to YouTube, outstream ads are a good option. They are billed on a vCPM basis, meaning you pay for viewable impressions, which makes them cost-effective.
3. Setting Up Your Google Ads Account
Creating a Google Ads Account
- Visit Google Ads: Navigate to the official Google Ads website via your web browser.
- Sign-Up Procedure: Click on the ‘Start Now’ button to initiate the process. You’ll be required to fill in details such as your business email and the website you wish to advertise. Follow the steps to complete account setup, which will involve setting your time zone, currency, and billing details.
Linking YouTube Channel
- Navigate to ‘Linked Accounts’: Once you’re logged into Google Ads, go to the ‘Settings’ and find the ‘Linked Accounts’ option.
- Follow Prompts to Link Account: Here, you can connect various accounts, including your YouTube channel. Click on the YouTube option and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the linking. This often involves logging into your YouTube account to confirm permissions.
4. Video Ad Creation
Video Content
- Relevance to Campaign: Your video content should align with your overall campaign goals. For example, if your campaign aims to increase product awareness, your video should focus on showcasing the product’s features and benefits. If the goal is customer engagement, consider creating content that prompts viewers to interact with your brand.
- Duration: Length is crucial. Too short, and you might not convey your message effectively; too long, and you risk losing the viewer’s attention. Aim for a 30-second to 1-minute duration for most campaigns. However, longer formats may be suitable for explainer videos or tutorials.
Uploading the Video
- To YouTube: Since Google Ads is integrated with YouTube, you’ll need to upload your video to your YouTube channel first. Make sure the video is set to ‘Public’ or ‘Unlisted’ to use it in your Google Ads campaign.
- Quality Check: Before uploading, double-check your video for quality, ensuring it meets YouTube’s video requirements, such as format, aspect ratio, and resolution.
Creating the Campaign
- Go to ‘Campaigns’: Log into your Google Ads account and navigate to the ‘Campaigns’ tab on the sidebar.
- Select ‘+ New Campaign’: You’ll be prompted to choose the type of campaign you wish to create. Select ‘Video’.
- Setting Objectives and Preferences: Choose your campaign objective, such as sales, leads, or website traffic. Then, set your target audience, geographical locations, budget, and more according to your preferences.
5. Audience Targeting
Demographics
- Age, Gender, Parental Status: You can specify the age range, gender, and parental status of the audience you wish to target. This ensures that your ads are relevant to the viewer, increasing the likelihood of engagement.
- Household Income: Another layer of demographic targeting includes household income levels, which can be particularly useful for high-ticket items.
Interests
- Affinity Audiences: These are users who have shown a strong interest in topics related to your industry. For instance, if you’re a fitness brand, you can target users who frequently visit health and fitness websites.
- In-Market Audiences: This targets users who are actively researching or planning to purchase a product or service like yours.
Keywords
- Broad or Exact Match: Keywords can be targeted based on their match type. Broad match will show your ad for related searches, while exact match will show your ad only for the specified keywords.
- Negative Keywords: These are terms for which you do not want your ads to appear. Use this feature to narrow down your audience and avoid irrelevant clicks.
6. Budget and Bidding
Daily Budget
- Setting the Limit: Daily Budget: Set your daily budget, which is the average amount you’re willing to spend each day on a campaign. Note that Google Ads may allow up to double the daily budget to be spent on a given day, but it will average out so you never exceed your set budget for the billing cycle.
- Campaign Total: You can also set a total budget for the entire campaign duration, allowing for greater control over spending.
Bidding Strategy
- Manual CPC & Automate bidding:
Manual CPC allows advertisers to set the highest amount they are willing to pay for a click. Alternatively, Automated Bidding lets Google automatically set bid amounts based on the likelihood that the ad will result in a click or conversion.
7. Analytics and Reporting
Metrics to Monitor
- View Rate & Viewability: View rate is calculated by taking the total views of your video ad and dividing it by the total number of impressions. It helps you understand how compelling your ad is to viewers. Additionally, viewability measures the percentage of your video ads that are actually viewed by users, meeting certain criteria such as being on screen for a specific amount of time.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): This metric shows the percentage of viewers who clicked on the call-to-action or companion banner in your video ad. A high CTR often indicates that the ad’s messaging aligns well with the audience’s intent.
- Cost-Per-View (CPV): This shows how much you pay each time someone views your video. Lowering your CPV while maintaining or increasing views is generally the goal.
- Watch Time: This metric indicates the total number of minutes that audiences have spent watching your video on YouTube. It’s a critical metric for understanding how engaging your video is beyond just the initial click.
Reporting Tools
- Google Ads Dashboard & Third-Party Tools: While the Google Ads Dashboard is essential for tracking campaign performance, you may also utilize third-party analytics tools that can be integrated for deeper insights.
- Google Analytics: For more advanced tracking, Google Analytics can be linked to your Google Ads account to provide more detailed user behavior data.
8. Tips and Best Practices
Ad Creative
- Strong Opening & Video Sequencing: The first few seconds are crucial for capturing attention. Video sequencing can also be used in Google Ads, which allows you to set a series of videos to play in a particular order, offering a storytelling approach to your campaigns.
- Clear Call-to-Action: Make sure your CTA is clear and compelling. Use action-oriented language like “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up Today.”
Optimization
- A/B Testing & Multivariate Tests: In addition to simple A/B testing, consider running multivariate tests that change multiple variables simultaneously to understand how they interact and affect performance. You can change one variable at a time, like the headline, CTA, or even the video content itself.
- Ad Extensions: Use ad extensions to provide additional information or links to specific sections of your website. This can improve the ad’s utility and increase the likelihood of clicks.
Ongoing Management
- Adjust Budgets and Bids: As your campaign progresses, regularly review and adjust your budgets and bids based on performance data.
- Content Refresh: Stale ads can decrease in effectiveness over time. Regularly update your ad creative to keep your messaging fresh and engaging.
9. Conclusion
Video advertising through Google Ads offers a flexible, scalable, and effective way to reach potential customers. From creating the ideal video ad content and choosing the right formats to targeting your audience and setting your budget, each step is critical to the success of your campaign. Regular monitoring and optimization are essential for achieving the best ROI. Whether you’re new to Google Ads or an experienced advertiser, the platform’s diverse capabilities allow for a tailored advertising approach that can meet various business goals and needs.