Introduction
In the fast-paced, ever-changing world of eCommerce, staying ahead of the competition is not merely a luxury; it’s a necessity. One of the most powerful tools at your disposal to achieve this is Google Ads. With its intricate algorithms, expansive reach, and customizability, Google Ads can be your game-changer. In this definitive guide, we will unravel the complexities and opportunities associated with Google Ads, focusing particularly on its application in eCommerce. From initial setup to advanced techniques, this is your one-stop resource.
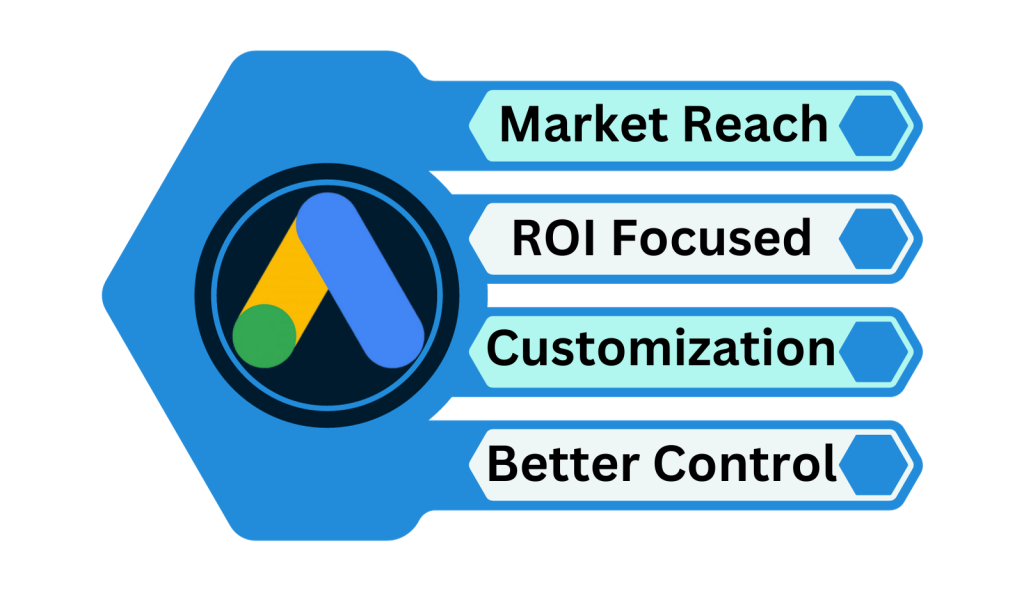
1. Understanding the Importance of Google Ads
a. Market Reach
Google is not just a search engine; it’s a cornerstone of the modern internet. With over 3.5 billion searches per day, Google offers a colossal audience. Through Google Ads, you can present your products or services to this massive user base, thereby significantly increasing the likelihood of attracting potential customers.
b. ROI Focused
The beauty of Google Ads lies in its pay-per-click (PPC) model, which ensures that your advertising spend is directly proportional to customer engagement. This financial model, combined with precise targeting features, can lead to high conversion rates and, consequently, a more cost-effective advertising strategy.
c. Customization
One size does not fit all when it comes to advertising. Google Ads offers an unparalleled level of customization. Whether you want to target users based on location, demographics, or even the devices they use, the Google Ads platform allows you to do so. This fine-grained control enables advertisers to craft strategies that align perfectly with their business objectives.
2. Account Structure and Setup
a. Campaign Level
Campaigns serve as the backbone of your Google Ads account. They are high-level containers that should be organized thoughtfully. You may choose to separate campaigns by product types, seasonal promotions, or target markets. The goal is to ensure that each campaign has a clear focus to make monitoring and optimization more manageable.
b. Ad Group Level
Within each campaign are multiple ad groups. These ad groups should be designed to be even more specific subsets of your campaign. For instance, if you have a campaign for winter clothing, one ad group could focus solely on winter jackets, while another could target winter boots. By doing this, you can create more relevant ads and landing pages for each group of keywords, thereby improving your Quality Score.
c. Keyword Lists
Creating the right keyword list is akin to crafting a secret recipe for success. Thorough keyword research should precede any ad group setup. The keywords you select must be aligned with the user intent and specific to each ad group. This will help improve ad relevance, click-through rates, and ultimately, your return on investment.

3. Budgeting and Bidding
a. Budget Allocation
The question of budget allocation can be daunting. Start by considering your overall marketing budget and how much you are willing to allocate specifically for Google Ads. This should be influenced by the average cost-per-click (CPC) in your industry and your sales margins. Proper budget allocation is essential for achieving your advertising goals without financial strain.
b. Bidding Strategies
Selecting the appropriate bidding strategy can have a massive impact on your campaign’s effectiveness. Google Ads offers several bidding strategies, including Cost-per-Acquisition (CPA), Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), and manual bidding. Understanding the nuances of each can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific objectives.
c. Cost Management
Managing costs effectively is pivotal in maintaining a sustainable Google Ads strategy. Regularly monitor your average CPC, conversion rates, and other key performance indicators. This ongoing oversight allows for real-time adjustments to your bidding strategy, ensuring you are always maximizing your return on investment while staying within budget.
4. Keyword Research and Selection
a. Importance of Keywords
Keywords act as the linchpin in your Google Ads strategy. When users search for products or services, it’s your chosen keywords that trigger your ads. Therefore, having the right keywords is critical for connecting with your target audience.
b. Types of Keywords
From broad match to exact match, the Google Ads platform offers different types of keyword matching options. Knowing when and how to use each can make a significant difference in reaching the right audience without wasting ad spend.
c. Long-Tail Keywords
Don’t underestimate the power of long-tail keywords. These are longer and more specific keyword phrases that visitors are more likely to use when they’re closer to making a purchase. They can often yield lower CPCs and higher conversion rates compared to broader keywords.
5. Ad Creation and Optimization
a. Ad Copy Relevance
The ad copy is the first thing a potential customer sees. It needs to be not only compelling but also relevant to the keyword and landing page. This relevance is crucial for maintaining a high Quality Score, which can result in lower CPCs.
b. Ad Extensions
Ad extensions provide additional information or links directly in your ad. This can include site links, callout extensions, or structured snippets, and can significantly improve your ad’s visibility and CTR.
c. A/B Testing
Never settle for your first draft of an ad. Always run A/B tests to compare different headlines, descriptions, and extensions. This enables you to identify the best-performing elements and incorporate them into your ongoing strategy.
6. Landing Page Optimization
a. Page Relevance
A landing page should deliver what the ad promises. If your ad talks about a specific product, the landing page should be focused on that product, not a general catalog. This boosts the user experience and improves conversion rates.
b. Page Speed
In the age of immediacy, loading speed can be a make-or-break factor. Slow-loading pages can lead to higher bounce rates and wasted ad spend. Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to identify and rectify any issues affecting your landing page speed.
c. Call to Action
A strong and clear Call to Action (CTA) is essential for guiding the user towards conversion. Whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or downloading a resource, your CTA should be concise, compelling, and prominent.
7. Bidding Strategies
a. Manual CPC
Manual Cost-Per-Click (CPC) allows you to set bids for different keywords. While this strategy offers great control, it also demands a lot of time and attention to manage effectively.
b. Automated Bidding
Google Ads offers various automated bidding strategies like Target CPA, Maximize Clicks, and Enhanced CPC. These options can automate bid adjustments based on real-time data, allowing you to focus on other aspects of your campaign.
c. Budget Management
Keeping track of your ad spend is crucial. Allocate budgets based on the performance and potential ROI of each campaign. Periodic reviews are necessary to redistribute budgets and maximize profitability.

8. Performance Tracking
a. Google Analytics Integration
Integrating Google Analytics with Google Ads provides a more comprehensive view of how your ads are performing. Metrics such as bounce rate, time on site, and conversion rate give valuable insights.
b. Conversion Tracking
Don’t just track clicks and impressions; keep an eye on actual conversions. This helps in understanding the ROI and effectiveness of each campaign.
c. KPI Monitoring
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA), Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), and Click-Through Rate (CTR) should be regularly monitored and analyzed to make data-driven decisions.
9. Scaling Your Campaigns
a. Geo-Targeting
Once a campaign shows promise, consider scaling it by expanding to other geographical locations. Use location data to identify high-performing areas.
b. Ad Scheduling
Run ads at different times and days to identify when your target audience is most active. Adjust your bidding strategy based on these insights to maximize reach and ROI.
c. Diversifying Ad Formats
Google Ads offers various formats like Search Ads, Display Ads, and Video Ads. Diversifying your ad formats can attract different segments of your target audience.
10. Continuous Improvement
a. Learning and Adapting
The digital advertising landscape is always evolving. Keep yourself updated with the latest trends and algorithm changes to adapt your strategies accordingly.
b. Periodic Audits
Regular audits of your Google Ads account can unearth underperforming campaigns or keywords. Use these insights for continuous improvement.
c. Future-Proofing
Stay ahead by planning for upcoming seasons, festivals, or events. Seasonal trends can offer lucrative opportunities if tapped into at the right time.
And there you have it—a comprehensive guide to mastering Google Ads for eCommerce. Each of these sections is crucial for building and maintaining a successful advertising campaign. By paying attention to each element, you set yourself up for success in the competitive world of online advertising.